lateral rectus muscle function
 Eye Muscles
Eye MusclesSubscribe Side Rectus - Musculus rectus lateralis Anatomical pieces illustrated with images of e-Anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures Anatomical hierarchy Rear Anatomical children Translations DescriptionOrigin: Anulus of Zinn at the orbital apex Origin: Insertion: 7 mm temporal to the corneal limbus Insertion: Nerve: Abducens nerve Nerve: Action: Abducts the eyeball Action: Description: The muscle of the lateral rectum is a muscle in the orbit. It is one of the six extraocular muscles that control the movements of the eye (abduction in this case) and the only muscle invaded by the abducens nerve, cranial nerve VI. Its function is to remove the student from the middle line of the body. It is clinically tested by asking the patient to look sideways. Description: lateral straight muscle The four Recti emerge from a fibrous ring (anulus tendineus communis) that surrounds the upper, medial and lower margins of the optical foramen and surrounds the optical nerve. The ring is completed by a long tendentious bridge over the lower and medial part of the upper orbital fissure and attached to a tubercle on the margin of the great wing of the sphenoid, tied to the fissure. Two specialized parts of this fibrous ring can be made: a lower part, the ligament or tendon of zinc, which gives origin to the lower Rectus, part of the Rectus internus, and the lower head of origin of the Rectus lateralis; and a top part, which gives origin to the superior Rectus, the rest of the Rectus medialis, and the upper head of the Rectus lateralis. This upper band is sometimes called the top tendon of Lockwood. Each muscle moves forward in the implicit position by its name, to be inserted by a tendentious expansion in the sclera, about 6 mm. from the margin of the cornea. Between the two heads of the lateral straight is a narrow interval, through which the two divisions of the oculomotor nerve, the nasociliar nerve, the abducent nerve and the ophthalmological vein pass. Although these muscles have a common origin and are inserted similarly in the sclera, there are certain differences that are observed in them in terms of their length and breadth. The Rectus Medialis is the widest, the lateral Rectus is the longest, and the upper Rectus is the thinst and narrowest. They picked up Zinn, Lockwood's top tendon. ImagesDownload e-AnatomyMobile and tablet users, you can download e-Anatomy in Appstore or GooglePlay. Subscribe now Discover our subscription plansPersonal data When you browse the IMAIOS website, cookies are placed in your browser. For some of them, your consent is necessary. Click on each cookie category to enable or disable your use. To benefit all the functionalities of IMAIOS, we advise to keep activation of all categories of cookies. If you want to use the connection through your Facebook or Google account, then you accept cookies placed by these third parties according to what you have agreed and consented to. These cookies allow you to obtain anonymous attendance statistics, as well as error reports during the site visit, to optimize your ergonomics, browsing and content. By deactivating these cookies, we will not be able to analyze site traffic or detect errors. As part of electronic learning when you see a video, our Vimeo service provider files cookies with your browser. By deactivating cookies, you may not see Vimeo videos. These cookies guarantee the proper functioning of the site, in particular the connection to your account (IMAIOS session cookies), site security () and online payment (). The website cannot work properly without these cookies. English Copyright © 2008-2021 IMAIOS SAS. All rights reserved.
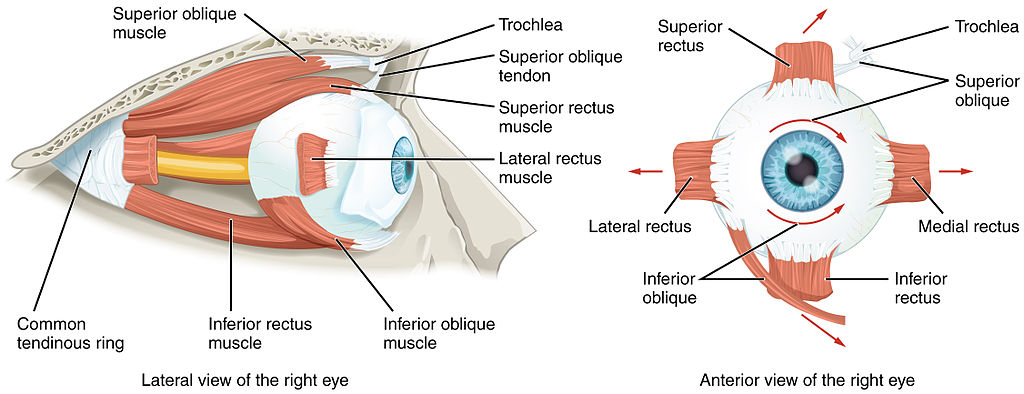
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Eye Medial Rectus Muscles Article

Muscles of Eye - Ophthalmology - Medbullets Step 2/3
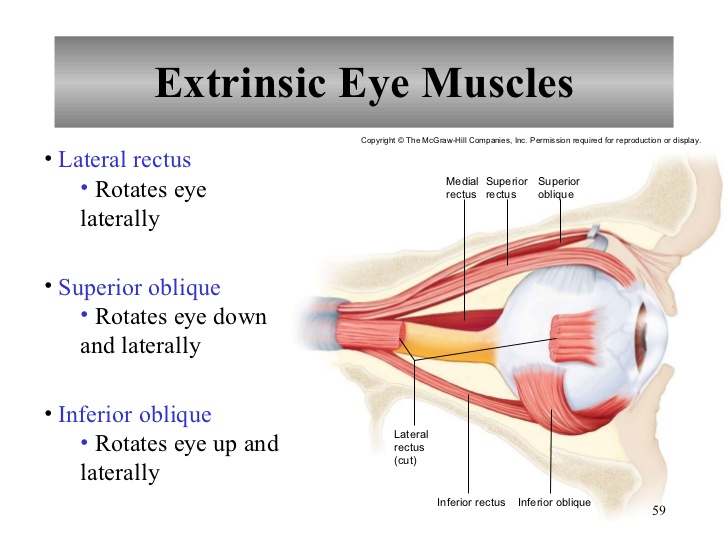
What are the 6 extrinsic muscles of the eye and their functions? | Socratic
Extrinsic muscles of the eyes

Muscles of Eye - Ophthalmology - Medbullets Step 2/3

Rectus muscle | anatomy | Britannica

Why is the abducens nerve called the lover's nerve? - Quora
Cardinal Positions of Gaze (Extraoccular movements) - Neuroanatomy Flashcards | Draw it to Know it
Extrinisic and Intrinsic Muscles of the Eye
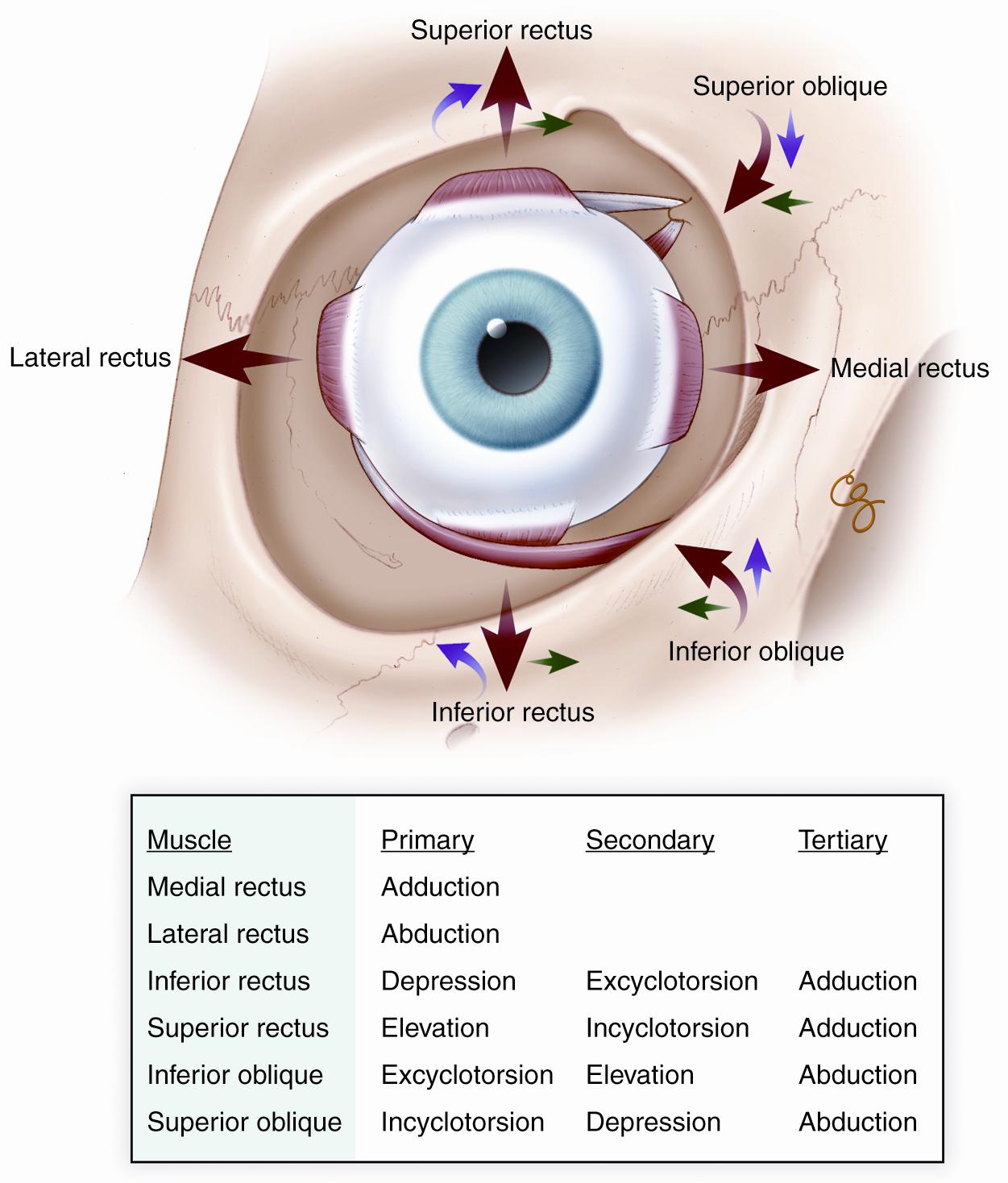
Extraocular Muscle Anatomy — Ophthalmology Review

Anatomy and Actions of the Extra-ocular (Eye) Muscles - Pediatric Ophthalmology PA

Lateral rectus muscle - Wikipedia

The Extraocular Muscles | Ento Key

A) Rectus extraocular muscles and the experimental design. One medial... | Download Scientific Diagram
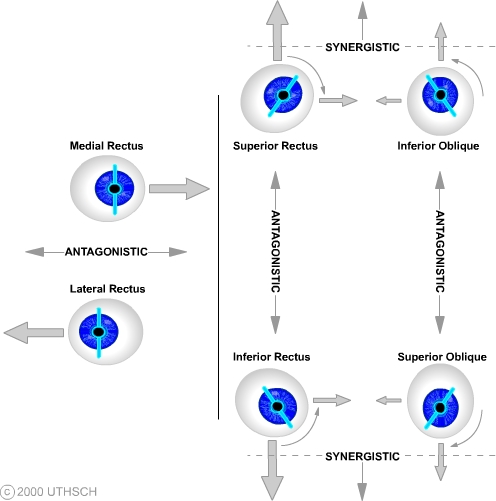
Ocular Motor Control (Section 3, Chapter 8) Neuroscience Online: An Electronic Textbook for the Neurosciences | Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy - The University of Texas Medical School at Houston

Anatomy of the Eye - American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus
Lateral rectus: Origins, insertions, actions, innervation | Kenhub
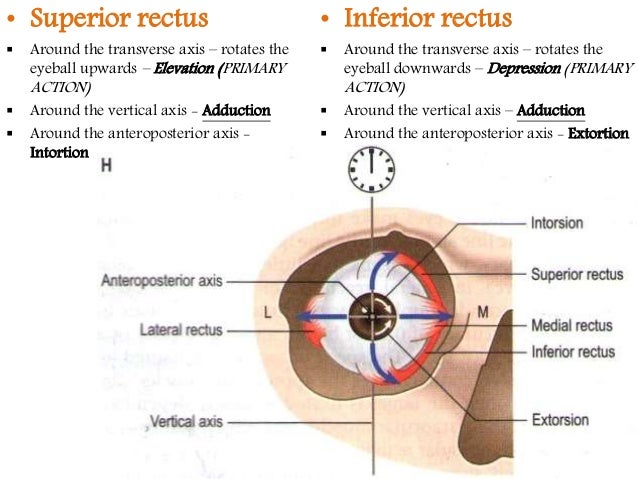
Extra ocular muscles ppt

MBBS Medicine (Humanity First): Extraocular Muscles : Function and Innervation
miss | eye muscle functions
PT on the Net
Extraocular Muscle Anatomy — Ophthalmology Review
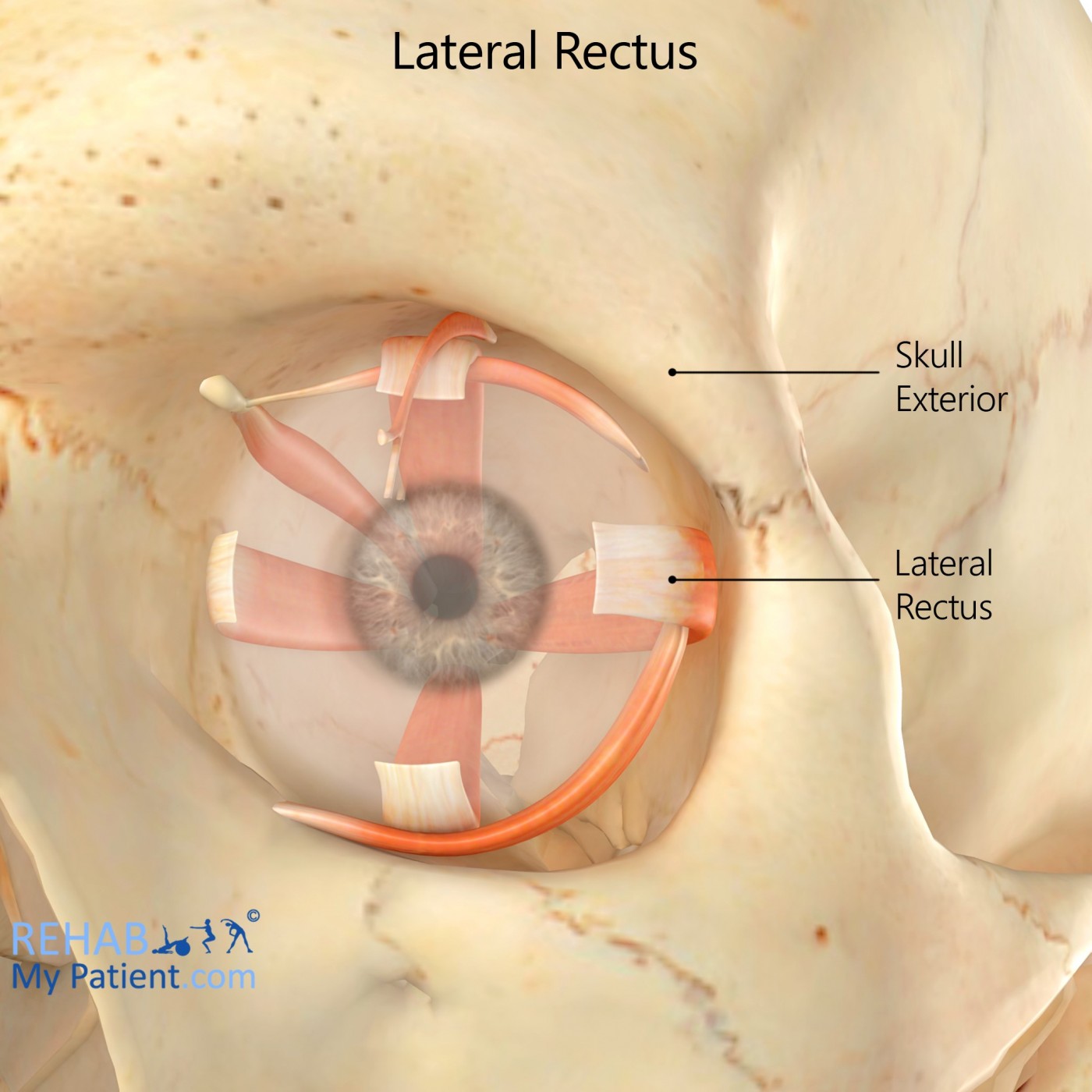
Lateral Rectus | Rehab My Patient

How to Assess the Six Cardinal Fields of Gaze

Rectus muscle | anatomy | Britannica

Extraocular Muscle Anatomy — Ophthalmology Review
AccessLange: General Ophthalmology ; Chapter 12, Page 1
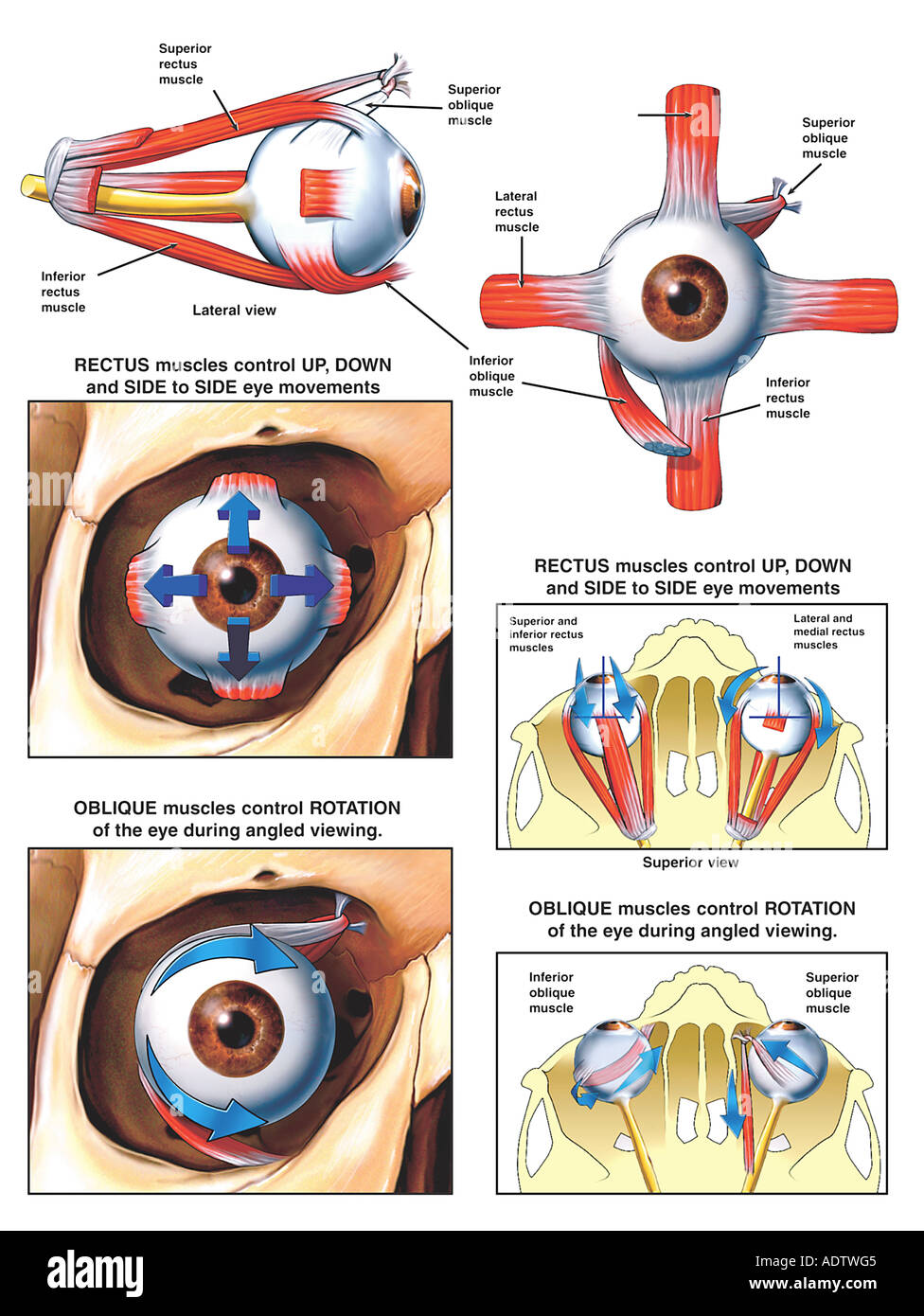
Anatomy and Function of the Eye Muscles Stock Photo - Alamy

HUM SAATH HAI - #Cranialnerve Examination #Abducens nerve... | Facebook
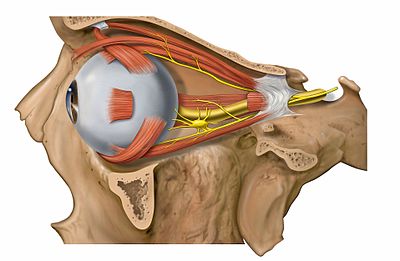
Extraocular muscles - Wikipedia

Dentistry lectures for MFDS/MJDF/NBDE/ORE: Lecture Notes for Muscles of the Head and Neck | Head muscles, Lectures notes, Shoulder muscle anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12552/Orbit.png)
Extraocular muscles: Anatomy and movements | Kenhub

NSE 22A/B Lecture Notes - Winter 2020, Lecture 6 - Palpebral Fissure, Lateral Rectus Muscle, Medial Rectus Muscle
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13023/FXZEHl1KYupJqsUh5hVew_M._rectus_lateralis_01.png)
Lateral rectus: Origins, insertions, actions, innervation | Kenhub
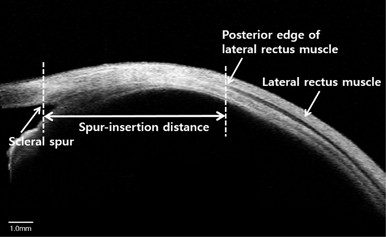
Postoperative change in lateral rectus muscle insertion measured by anterior segment optical coherence tomography | Eye
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/medial-rectus-muscle/v1278RK6rEeGs2IHyRttNA_CnQGa32KYARQsE89v1XFVw_M._rectus_medialis_01.png)
Medial rectus: Origin, insertion, innervation, action | Kenhub

Superior rectus muscle - Wikipedia

Cranial nerve palsies - AMBOSS
The Cranial Nerves (Organization of the Central Nervous System) Part 4
Medial rectus: Origin, insertion, innervation, action | Kenhub
Posting Komentar untuk "lateral rectus muscle function"